The Microscope in Cell Studies (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: 9700
Microscope slide preparation
Preparing a microscope slide
Specimens can be viewed under a light microscope; this allows some details of cellular material to be observed
Pre-prepared permanent slides can be viewed
Such slides are produced by cutting very thin layers of tissue which are stained and permanently mounted on a glass slide for repeated use
Different methods will be used to view different types of specimen, e.g. temporary slide preparations can be produced in the school laboratory as described below
Preparing a slide using a liquid specimen
Add a few drops containing the liquid sample to a clean slide using a pipette
Lower a coverslip over the specimen and gently press down to remove air bubbles
Coverslips protect the microscope lens from liquids and help to prevent drying out
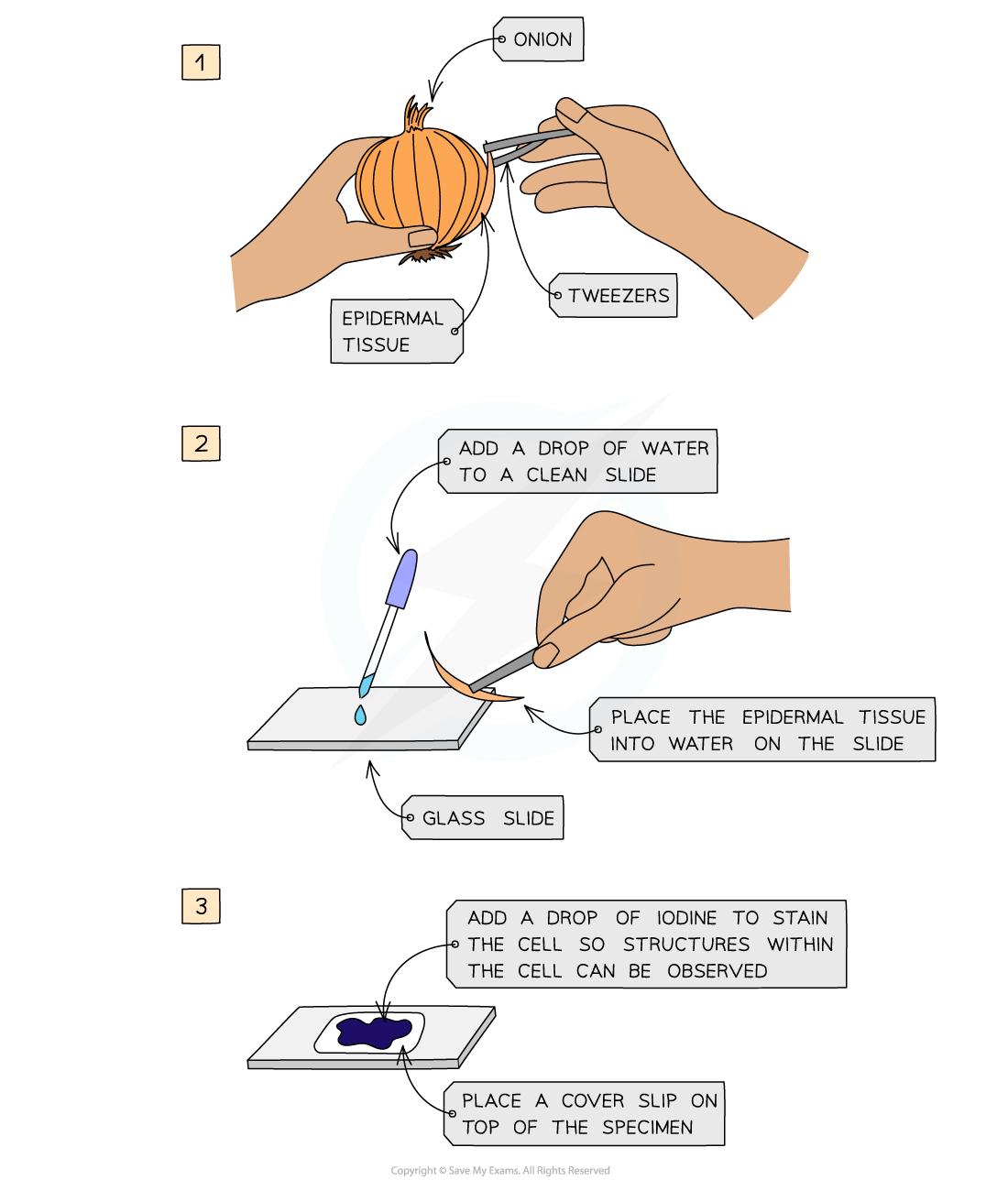
Preparing a microscope slide using a solid specimen
Use scissors or a scalpel to cut a small sample of tissue, and peel away or cut a very thin layer of cells from the tissue sample
The preparation method always needs to ensure that samples are thin enough to allow light to pass through
Place the sample onto a slide
A drop of water may be added at this point
Apply iodine stain
Gently lower a coverslip over the specimen and press down to remove any air bubbles
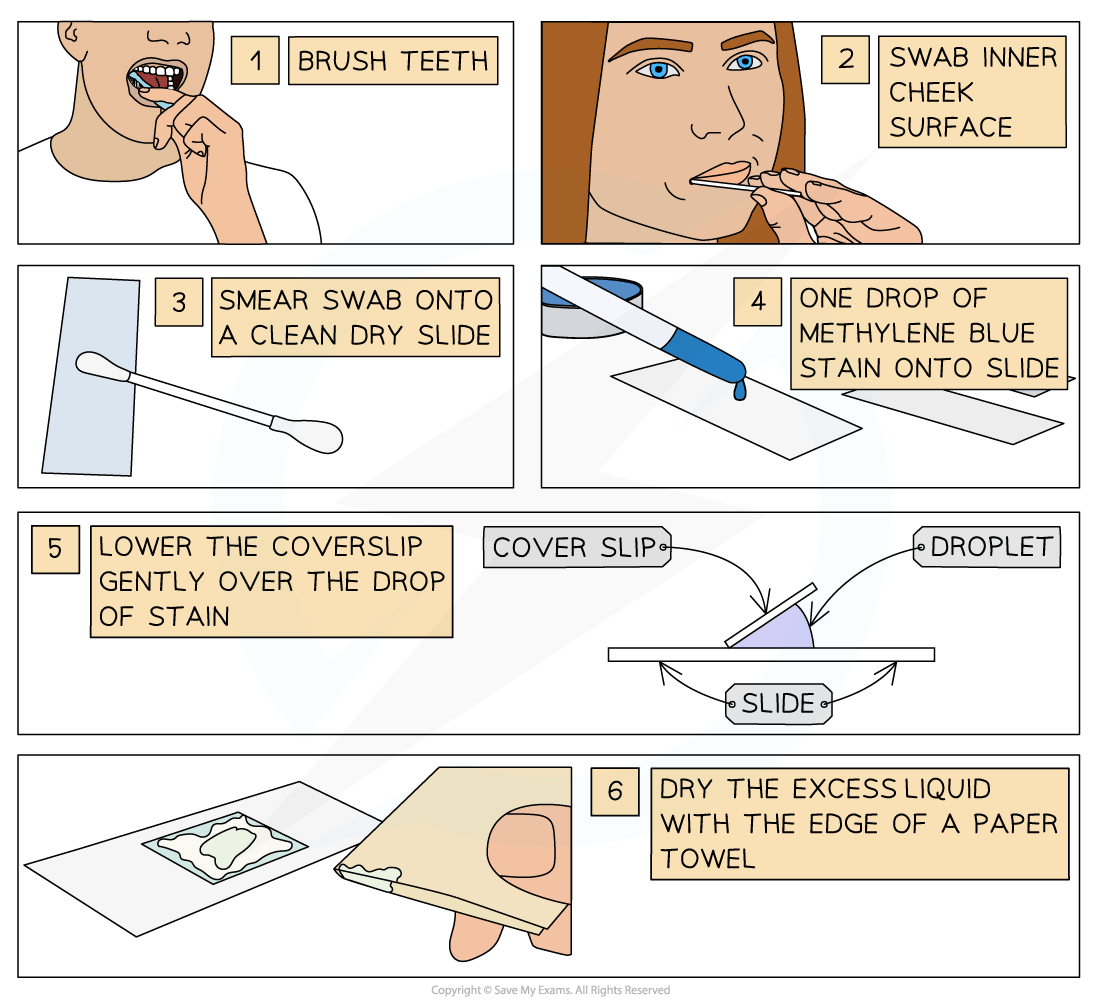
Preparing a slide using human cells
Brush teeth thoroughly with normal toothbrush and toothpaste
This removes bacteria from teeth so they don't obscure the view of the cheek cells
Take a sterile cotton swab and gently scrape the inside cheek surface of the mouth for 5-10 seconds
Smear the cotton swab on the centre of the microscope slide for 2-3 seconds
Add a drop of methylene blue solution
Methylene blue stains negatively charged molecules in the cell, including DNA and RNA
This causes the nucleus and mitochondria to appear darker than their surroundings
Place a coverslip on top
Lay the coverslip down at one edge and then gently lower the other edge until it is flat
This reduces bubble formation under the coverslip
Absorb any excess solution by allowing a paper towel to touch one side of the coverslip
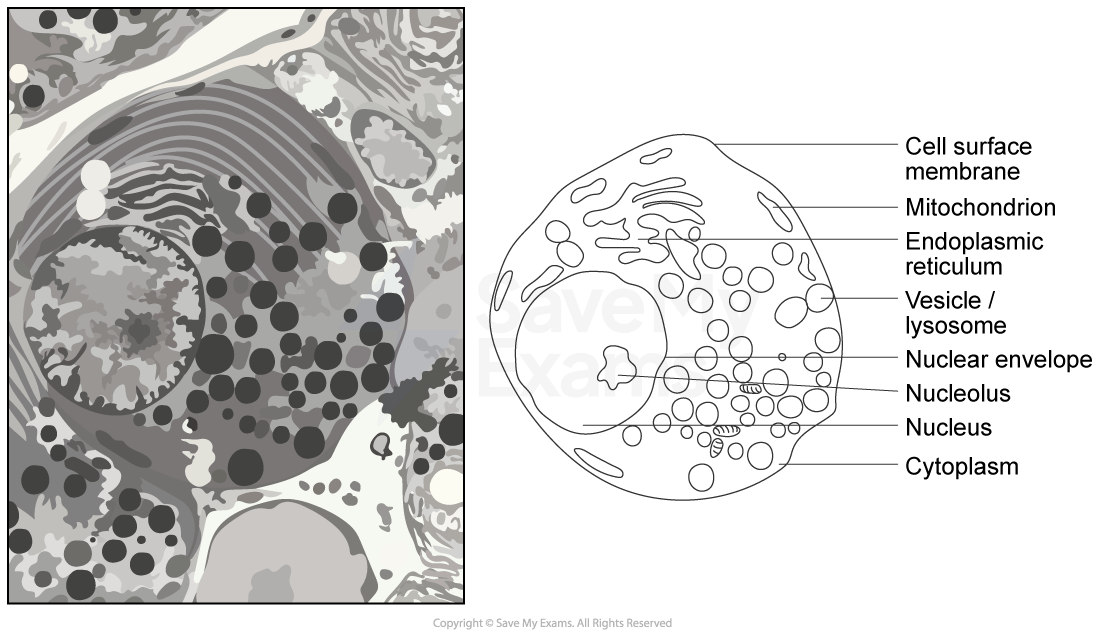
Drawing cells
To record the observations seen under a microscope, a labelled biological drawing is often made
Biological drawings are line drawings which show specific features that have been observed when the specimen was viewed
There are a number of rules/conventions that are followed when making a biological drawing
The drawing must have a title
The magnification under which the observations shown by the drawing are made should be recorded if possible
A scale bar may be used
A sharp pencil should be used
Drawings should be on plain white paper
Lines should be clear, single lines without sketching
No shading should be used
The drawing should take up as much of the space on the page as possible
Well-defined structures should be drawn
Only visible structures should be drawn, and the drawing should look like the specimen
The drawing should be made with proper proportions
Structures should be clearly labelled with label lines that:
Do not cross
Do not have arrowheads
Connect directly to the part of the drawing being labelled
Are on one side of the drawing
Are drawn with a ruler
Drawings of cells are typically made when visualizing cells at a higher magnification power, whereas plan drawings are typically made of tissues viewed under lower magnifications (individual cells are never drawn in a plan diagram)

Examiner Tips and Tricks
When producing a biological drawing, it is vital that you only ever draw what you see and not what you think you should see!

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?