Surface Area to Volume Ratios (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Biology)
Revision Note
Principles of SA:V
Surface area and volume are both very important factors in the exchange of materials in organisms
The surface area refers to the total area of the organism that is exposed to the external environment
The volume refers to the total internal volume of the organism (total amount of space inside the organism)
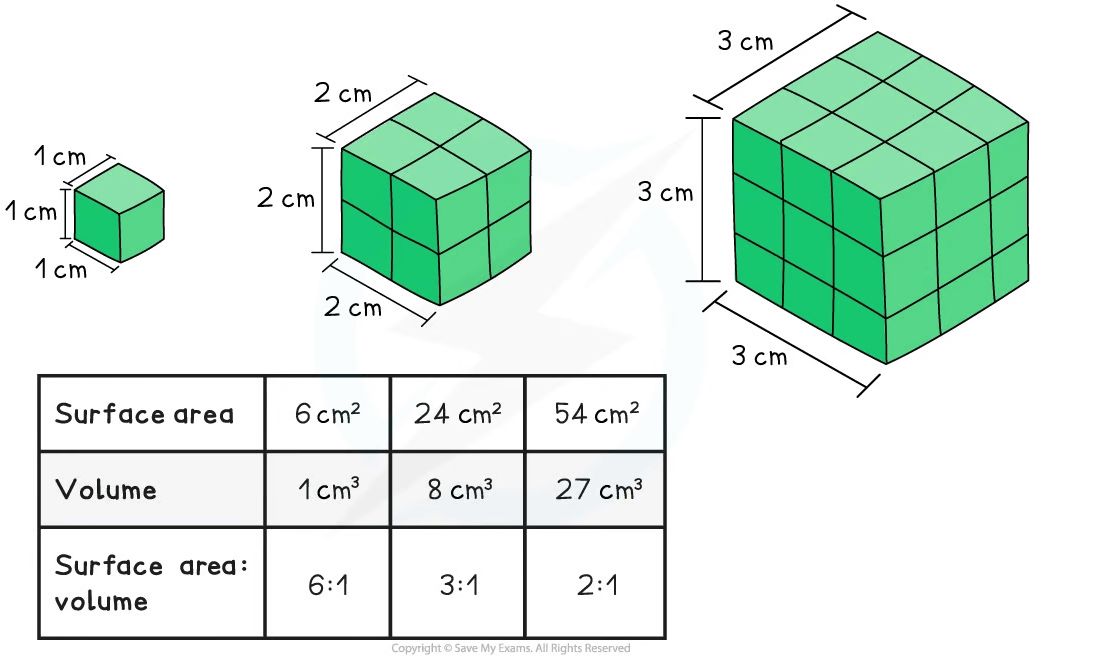
As the surface area and volume of an organism increase (and therefore the overall ‘size’ of the organism increases), the surface area : volume ratio decreases
This is because volume increases much more rapidly than surface area as size increases
Importance of a High Surface Area to Volume Ratio
Having a high surface area to volume ratio increases the ability of a biological system to perform the following important functions
Obtaining necessary resources eg, oxygen, glucose, amino acids
Eliminating waste products eg. carbon dioxide, urea
Acquiring or dissipating thermal energy (heat)
Otherwise exchanging chemicals and energy with the surroundings eg. absorbing hormones at the cell surface in the hormone's target organ
How Surface Area-to-Volume Ratio Changes With Size Diagram
As size increases, the surface area : volume ratio decreases
Calculating Surface Area to Volume Ratios Table
| Cube | Cuboid | Cylinder |
|---|---|---|---|
|  |  |  |
Surface Area | 6s2 | 2lh + 2lw + 2wh | |
Volume | s3 | l × w × h | |
Example | If s = 1 cm then SA = (1×1)×6 SA = 6cm2 V = s3 = 13 =1cm3 ∴ SA:V ratio = 6:1 | If l = 4cm, w = 2cm, h = 1cm, then SA = 2((4×1)+(4×2)+(2×1)) = 28cm2 V = 4 × 2 × 1 = 8cm3 ∴ SA:V ratio = 28:8 = 3.5:1 | If r = 2 cm and h = 6cm, then SA = 2πrh + 2πr2 = 8π +24π = 32π cm2 V = π(2)2 × 6 = 24π cm2 ∴ SA : V ratio = 32 : 24 = 1.33:1 |
The surface area:volume ratio calculation differs for different shapes (these shapes can reflect different cells or organisms)
Worked Example
Calculate the surface area-to-volume ratios of the two following microorganisms:
A bacterial cell from the species Staphylococcus aureus; you can assume that each cell is a cube with side length of 800 nm (8 × 10-9 m)
A bacterial cell from the species Bacillus subtilis; these are rod-shaped cells which you can assume to be cylindrical in shape. They are 5 µm long and 1 µm in diameter
Comment on your calculated answers.
Solution
1. For the Staphylococcus aureus cell: side length = 800 nm
Convert this value into µm by dividing by 1000
Surface area of cube = 6(s2)
= 6 × (0.8 × 0.8) = 3.84 µm2
Volume = 0.8 × 0.8 × 0.8
= 0.512 µm3
A ratio is one number divided by another with the larger number divided by the smaller number, so
___________
2. For the Bacillus subtilis cell: radius = 0.5 µm (half of diameter 1µm)
Surface area of a cylinder = 2πrh + 2πr2
= (2π × 0.5 × 5) + (2π × 0.52)
= 15.708 + 1.571 µm2
= 17.278 µm2
Volume of a cylinder: formula is πr2h
= π × 0.52 × 5
= 3.927 µm3
The cuboid cell of Staphylococcus aureus has a surface area-to-volume ratio of 7.5 : 1
The cylindrical cell of Bacillus subtilis aureus has a surface area-to-volume ratio of 4.4 : 1
The smaller cell has the largest surface area-to-volume ratio of the two shapes. This allows efficient diffusion into / out of the cell. Think of how long it might take to diffuse out of cell if a molecule starts its diffusion pathway right in the centre of the cell; the shortest distance to the edge will always be found in a cube. In a long cylinder, a molecule may travel parallel to the straight sides and so will have travel further to diffuse out (remember that molecular movement is random). So the larger the surface area to volume ratio, the better adapted to simple diffusion that organism is.
Examiner Tips and Tricks
This worked example assumes that Staphylococcus aureus is a cuboid shaped cell; in fact it is a spherical cell. You are not required to know how to calculate the surface area and volume of a sphere for this exam. A sphere has the highest surface area to volume ratio of any shape of a given radius/size, so is the best-adapted shape for diffusion.
However, you are expected to be able to calculate the SA:V ratio for a cube, cuboid or cylinder and explain how the increasing size of an organism affects the SA:V ratio.

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
