Name the monomer present in:
(i) cellulose
[1 mark]
(ii) starch
[1 mark]
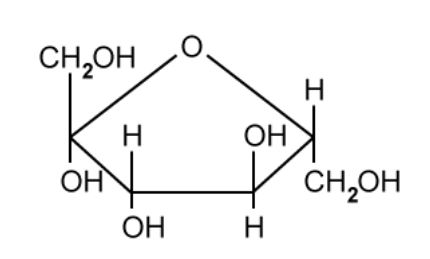
Figure 1 shows a molecule of alpha glucose. Beta glucose is an isomer of alpha glucose.
Figure 1

Draw a molecule of beta glucose.
A disaccharide is formed by a condensation reaction between two monosaccharides.
Identify molecules A and B in the word equation below and name the type of bond present in the resulting disaccharide.
alpha glucose + A ⟶ sucrose + B
Cotton is a plant fibre used to make cloth.
Explain how cellulose gives cotton its strength.
Was this exam question helpful?